PFAS Waste Management in Industrial Operations to Minimize Environmental Harm
PFAS Waste Management in Industrial Operations to Minimize Environmental Harm
Blog Article
Your Overview to PFAS Therapy Technologies and Advantages
The frequency of PFAS contamination in water resources requires a detailed understanding of offered therapy modern technologies. Each modern technology not only targets certain PFAS compounds however additionally plays an important function in enhancing total water high quality and protecting ecological integrity.
Recognizing PFAS Contamination
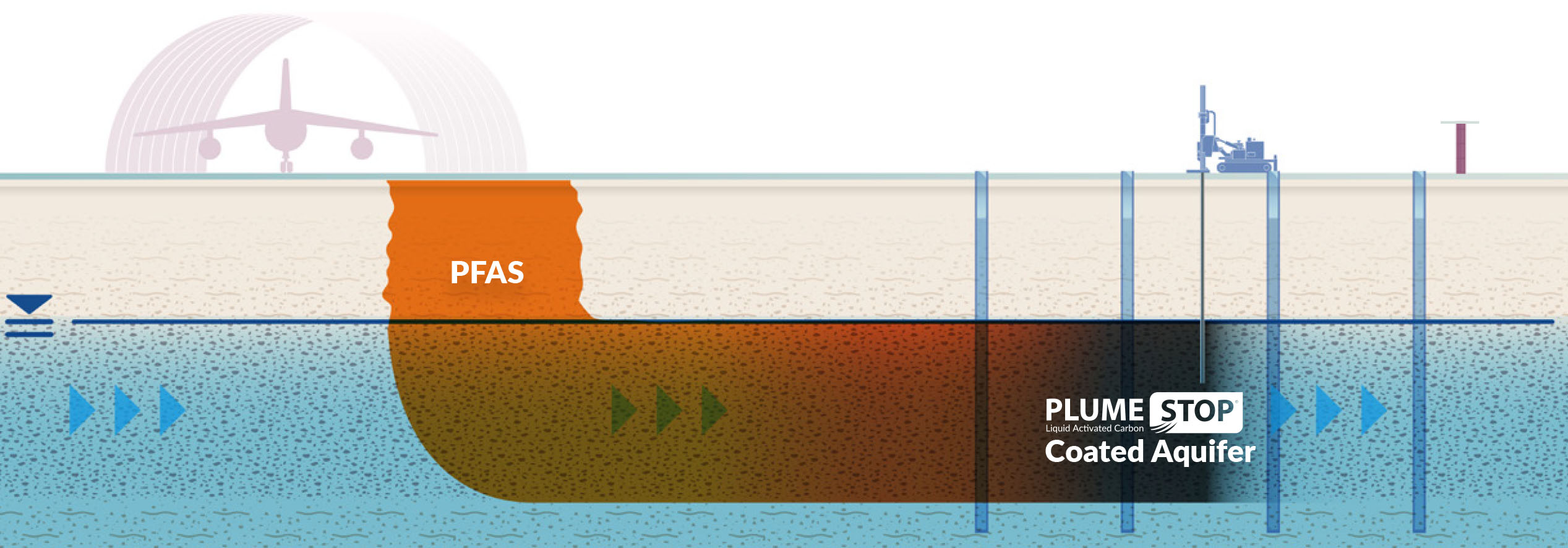
Comprehending PFAS contamination is important for resolving its pervasive effect on ecological and human wellness (m270 pfas treatment). Per- and polyfluoroalkyl compounds (PFAS) are a group of artificial chemicals commonly made use of in various industrial and consumer products because of their water- and grease-resistant homes. Generally discovered in firefighting foams, non-stick pots and pans, and water-repellent materials, PFAS have entered the atmosphere with production procedures, wastewater discharges, and seeping from land fills
As soon as released, these materials linger in the environment, causing extensive contamination of dirt and water resources. Their one-of-a-kind chemical structure, identified by solid carbon-fluorine bonds, renders them immune to destruction, leading to a phenomenon understood as "permanently chemicals." As a result, PFAS can build up in the human body and the food web, potentially creating negative health impacts, consisting of body immune system disruption, developing issues, and a boosted danger of certain cancers cells.
Regulatory companies and health organizations are progressively identifying the relevance of PFAS contamination, triggering efforts to check, evaluate, and alleviate its results. Understanding the pathways of PFAS contamination is vital for educating public law and developing reliable techniques to shield both environmental and human health and wellness.
Overview of Therapy Technologies
Numerous treatment technologies have been developed to attend to the challenges presented by PFAS contamination in water and dirt. These technologies can be generally classified right into numerous classifications, each with its unique systems and performance in eliminating PFAS compounds.
One famous approach is ion exchange, which uses material products to capture and get rid of PFAS from polluted water. This technique is specifically reliable for short-chain PFAS and can accomplish considerable reductions in concentration levels. One more innovation, advanced oxidation procedures (AOPs), utilizes strong oxidants and ultraviolet light to break down PFAS into less hazardous materials. AOPs appropriate for dealing with a wide variety of PFAS compounds yet may need careful optimization to make best use of efficacy.

Turned On Carbon Filtration
Turned on carbon purification is a commonly used approach for the elimination of PFAS from contaminated water, understood for its ability to adsorb a broad array of natural compounds. This innovation employs activated carbon, an extremely porous material with a substantial surface area, which assists in the binding of PFAS molecules via physical adsorption. The performance of turned on carbon in eliminating PFAS is affected by numerous variables, including the type of carbon utilized, the contact time, and the focus of PFAS in the water.
One of the benefits of turned on carbon filtration is its flexibility; it can be executed in different arrangements, such as granular activated carbon (GAC) systems or powdered triggered carbon (PAC) systems. GAC systems are normally used in larger-scale applications, while PAC can be utilized in smaller or short-lived configurations. In addition, the innovation is relatively simple to operate and keep, making it obtainable for several water therapy facilities.
Ion Exchange Systems
Ion exchange systems stand for one more effective technique for the elimination of PFAS from infected water, complementing methods like turned on carbon filtering. These systems operate the concept of trading ions in the water with ions hung on a resin material. Ion exchange materials can be particularly formulated to target the negatively charged PFAS compounds, effectively recording them and allowing cleaner water to pass through.
Among the primary advantages of ion exchange systems is their ability to eliminate a large range of PFAS, including both long-chain and short-chain versions. This adaptability makes them suitable for various applications, varying from local water treatment to commercial procedures. Additionally, ion exchange systems can usually accomplish reduced discovery restrictions for PFAS contrasted to some other treatment techniques, therefore improving water high quality.
Nevertheless, it is necessary to monitor and handle the regeneration of ion exchange media, as the performance can decline over time because of saturation. Correct upkeep and replacement of the resin are vital for maintaining the system's efficiency. Website Generally, ion exchange systems provide my blog a trustworthy and efficient remedy for PFAS removal, contributing considerably to secure drinking water criteria and environmental management.
Advanced Oxidation Processes
Advanced Oxidation Processes (AOPs) use powerful oxidants to effectively degrade PFAS substances in infected water. These ingenious therapy methods create very reactive varieties, such as hydroxyl radicals, that can damage down intricate PFAS particles right into much less harmful by-products. m270 pfas treatment. AOPs commonly use mixes of ultraviolet (UV) light, ozone, hydrogen peroxide, or Fenton's reagent, boosting the oxidation capacity and improving destruction efficiency
The main benefit of AOPs hinges on their capacity to target a broad array of PFAS compounds, consisting of both long-chain and short-chain versions. This convenience is crucial, as PFAS contamination commonly entails mixtures of various compounds with varying chemical frameworks. Moreover, AOPs can be integrated into existing water therapy systems, making them a useful solution for lots of municipalities and markets.
However, the execution of AOPs can be resource-intensive, requiring cautious consideration of operational prices and power consumption. In addition, while AOPs work in damaging down PFAS, they may not totally eliminate all byproducts, demanding more treatment steps - m270 pfas treatment. Generally, AOPs represent an encouraging avenue for addressing PFAS contamination, adding to cleaner water resources and enhanced public wellness protection

Conclusion
By picking the ideal innovation, communities can boost water quality, protect public health, and reduce the ecological dangers connected with PFAS direct exposure. Continued redirected here research study and implementation of these methods are important for reliable monitoring of PFAS contamination in influenced locations.
Report this page